How to connect PCIe SSD to Motherboard?
PCIe SSD's are solid state drives which do not use the Motherboards SATA Chipset interface to communicate between the SSD and the Windows File system.
NVMe SSD is using PCIe as the data transmission I/O channel. PCIe NVMe SSDs are not SATA drives, though some may share one or more aspect with SATA drives.
There are a number of ways you can connect a PCIe NVMe SSD to your Motherboard:
1. An M.2 slot.
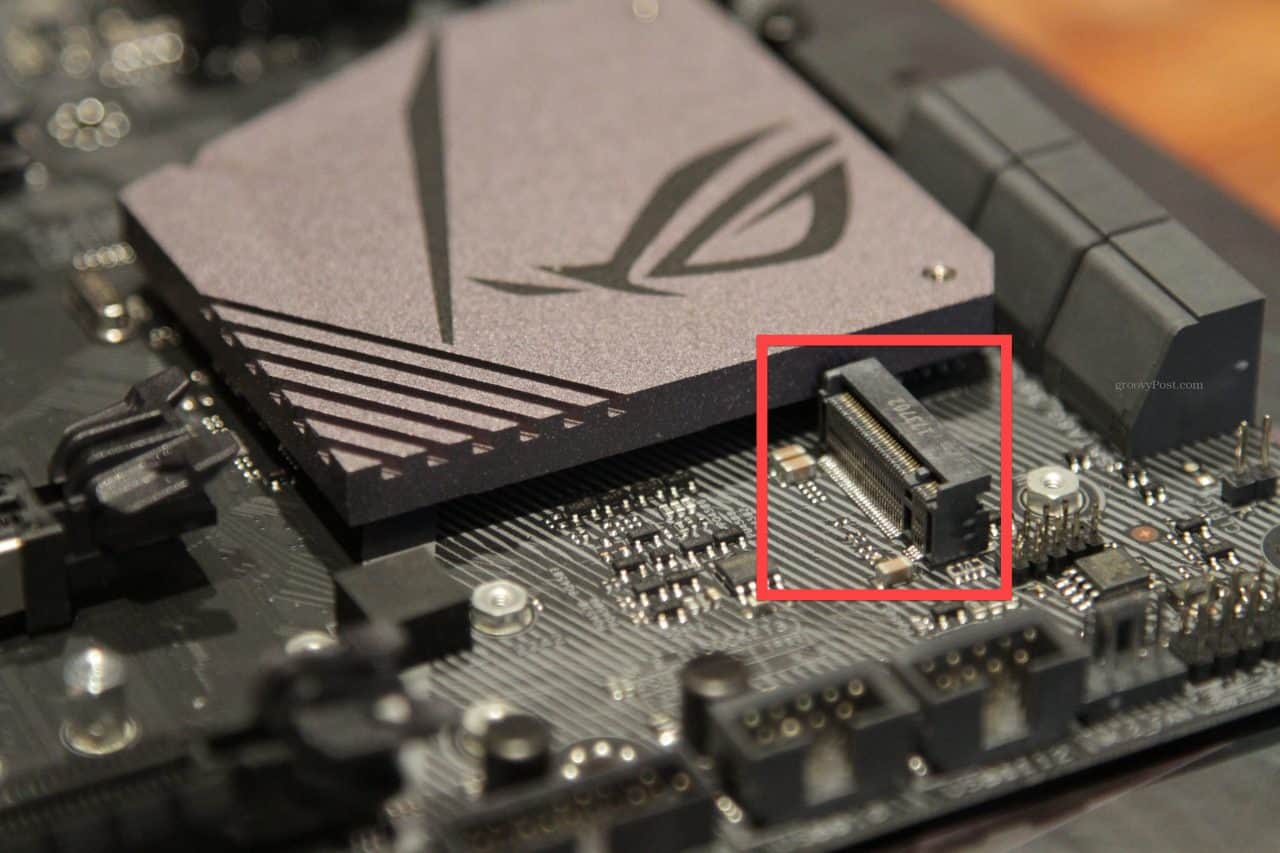
M.2 slot is suitable for PCIe NVMe SSD with M.2 interface.
2. A Standard PCIe slot. (One that is at least x4)

For Standard PCIe slot, there are sereral ways to connect PCIe NVMe SSD to your motherboard.
a) A PCIe to SFF-8643 adapter card and cable, that is connected to SSD integrate a U.2 interface.

b) A PCIe to U.2 slot adapter card.

c) A PCIe to M.2 slot adapter card.

PCIe SSDs increase performance by getting rid of the SATA interface (Which so far has a maximum of 10 channels.) for PCIe. (Which currently has a maximum of 25 channels.) This makes it particularly suitable for buffering and caching applications. PCIe is a multipurpose bus designed to put through all kinds of data to the processor. However it's lack of specialisation makes programming difficult. This means you could see a trade off between interoperability and performance.
There are two types of non-Physical Interface. AHCI and NVMe.
AHCI
(Advanced Host Controller Interface) is the same protocol used by SATA SSDs.
NVMe
(Non Volatile-Memory Express) is a protocol designed specifically for SSD storage. It shares nothing with SATA and replaces AHCI with a better method of dealing with solid state storage. PCIe NVMe SSDs also have their own NVMe storage controller built into the drive.



